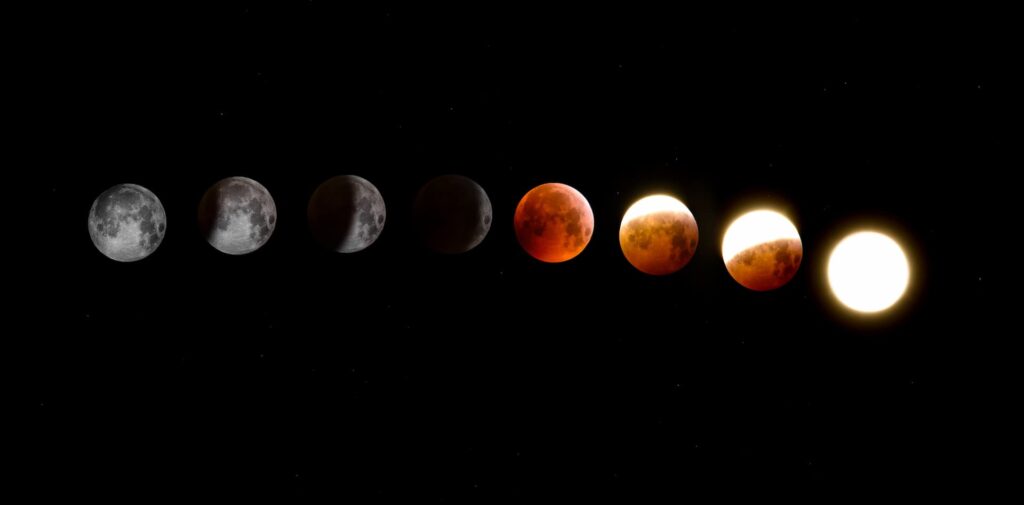
Physics and astronomy
Physics and astronomy are the most ancient sciences of nature. The sights of human culture found in various parts of the globe are evidence of the fact that ancient interest of man in phenomenon of nature. The needs of life, as well as the curiosity known to each of us, forced a person to observe natural phenomena. Especially people were attracted by the starry sky, which still remains mysterious and unknown.
The first ideas about the universe were very naive, they were closely intertwined with religious beliefs, which were based on the division of the world into two parts – earthly and heavenly. If now every child knows that the Earth is a heavenly body, then earlier “earthly” was opposed to “heavenly”. People thought that there was a “firmament of heaven” to which the stars were attached, and the Earth was taken for the motionless center of the universe.
The emergence of the natural sciences But, in the end, thanks to human activity, so much knowledge accumulated that it led to the birth of the first sciences. The first physicists were Greek thinkers who tried to explain the observed phenomena of nature. The most prominent of the ancient thinkers was Aristotle (384-322 BC), who introduced the word “fusis”, which in Greek means nature. Even in ancient times, methods of scientific knowledge of nature began to develop (observation, assumption (hypothesis), modeling, thought experiment, etc.). All natural-mathematical sciences—physics, astronomy, chemistry, geography, biology, and mathematics—began their development from the works of scientists-philosophers of the ancient period. The development of mathematics, geography, p hysics, chemistry and others, if not directly, then indirectly, was associated with the successes and demands of astronomy in study of celestial bodies.
In the II century. n. e. The Alexandrian astronomer Ptolemy proposed a geocentric (“geo” – earth) “system of the world.” Around the Earth, according to Ptolemy, move (in order of distance from the Earth) Moon , Mercury , Venus, Sun , Mars , Jupiter , Saturn, stars. But already at that time, visible observations of the motion of the Moon, the Sun, and the planets indicated that this motion was much more complicated. Therefore, each of the planets, according to Ptolemy, moves not just around the Earth, but around a certain point, which, in turn, moves in a circle, around the Earth. The Ptolemaic system of the universe was (under the auspices of the church) dominant in science for fourteen centuries. The first to offer new views on the universe were the great Italian scientists Nicholas of Cusa and Leonardo da Vinci , who argued that the Earth moves, that it is not the center of the Universe and does not occupy an extraordinary place in it.
The brave scientist who “moved the Earth, stopped the Sun” was the Pole Nicolaus Copernicus (1473-1543). The heliocentric (“helio” – the Sun) “system of the world” of Copernicus was not recognized by the church. According to the verdict of the Inquisition, in 1600, an outstanding Italian philosopher, a follower of Copernicus, Giordano Bruno (1548-1600), was burned in Rome, who, developing the teachings of Copernicus, argued that there is no and cannot be a center in the Universe, that the Sun is only center of the solar system. He also expressed a brilliant conjecture that the stars are the same “suns” as ours, and planets move around them, many of which have life.
Development of physics and astronomy
Initial data about fundamental physical theories formed the basis of modern physics and astronomy. From the middle of the XVI century. a qualitatively new stage in the development of physics begins – researchers begin to apply experiments and experiences. A powerful impetus to the formation of physics and astronomy as sciences was the scientific work of Isaac Newton. In his work “The Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy” (1687), he develops a mathematical apparatus for explaining and describing mechanical phenomena. On the laws formulated by him, the so-called classical (Newtonian) mechanics was built. And the famous law of universal gravitation laid the foundations of celestial mechanics. Newton’s genius lies in the fact that he proved the universality of the force of gravity, or gravity, that is, that the same force that acts on an apple during its fall to Earth, The moon, which revolves around the earth, also attracts. The force of gravity controls the movement of stars and galaxies, and also affects the evolution of the entire universe. The principle of inertia discovered by Galileo Galilei, the law of universal gravitation by Isaac Newton and the general theory of relativity by Albert Einstein – all these discoveries were later confirmed on the basis of astronomical data.
The influence of physics on technological progress

Rapid progress in the study of nature, revelation of new phenomena and laws of nature contributed to the development of society. Since the end of the 18th century, the development of physics has caused a rapid development of technology. At this time, steam engines appeared and improved. Due to their wide use in production and transport, this period of time is called the “epoch of steam”. At the same time, thermal processes are being studied in depth, and a new branch is being singled out in physics—thermodynamics. Many new discoveries are also taking place in the field of electricity and magnetism, which contributes to the development of the so-called classical electrodynamics, which explained the properties of electromagnetic fields, the electromagnetic nature of light.
At the end of the XIX and at the beginning of the XX century. electric machines appear and improve. Due to the widespread use of electrical energy, this time is called the “epoch of electricity”. In physics, new sections are distinguished – electrodynamics, electrical engineering, radio engineering, etc. At the beginning of the XX century. physicists obtained numerous experimental results that could not be reconciled with the provisions of classical mechanics and electrodynamics. A new stage of development begins in physics—the creation of quantum and relativistic theories. People have learned how to extract and widely use nuclear energy , explore outer space, design new automated devices and mechanisms. 20th century called “atomic age”, “space age”. In physics, intensive research is being carried out on the atomic nucleus, plasma, controlled thermonuclear reactions, semiconductors, and the like. Astronomy is developing intensively through the use of physical research.
Beginning of the 21st century accompanied by a huge breakthrough in the field of information technology, satellite communications, nanotechnology. But the basis in any field of engineering and technology is the laws of physics. Astronomy is closely related to other and natural sciences. On astronomical research, all the fundamental laws of physics are used, the methods of physics, mathematics, Chemistry and related sciencesare widely used. A feature of astronomy in comparison with other natural sciences is that it is predominantly an observational science. It can also be called a consumer of physical achievements and computer technology. At the same time, astronomy is a progressive science that enriches physics and chemistry with the results of studies of matter under such physical conditions ( temperature , pressure, magnetic field, etc.) that cannot be reproduced in terrestrial laboratories.
Conclusion
The ideological potential of the natural sciences has been tremendous. Physics and astronomy are not just the result of painstaking and inquisitive work of scientists, but also a great asset of human civilization, an important component of human culture. First of all, physics provides systematized information about the surrounding world along with the ability to obtain such information. Therefore, its methods and theories are widely used by other sciences, and most of all by astronomy.